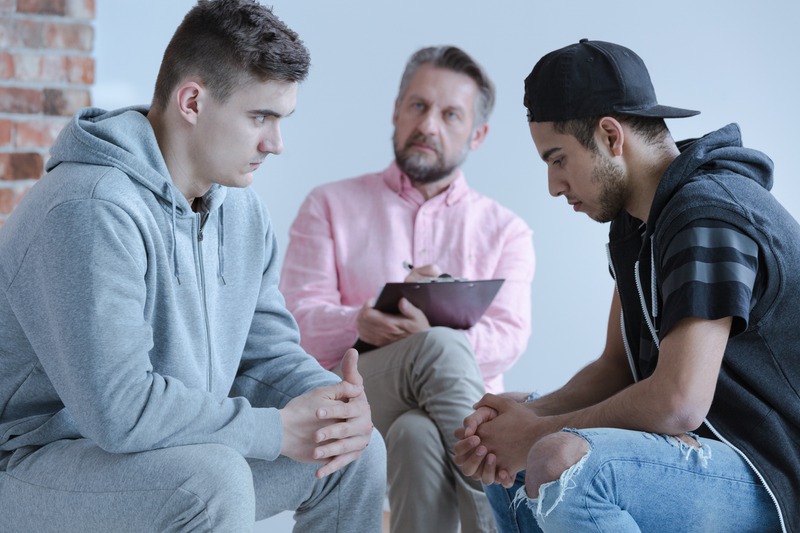
Addiction treatment remains a vital step in the recovery journey for those grappling with substance abuse issues. Treatment modalities fall into two broad categories: inpatient and outpatient care. Outpatient treatment programs, though demanding, allow patients to maintain their daily routines, including work or school commitments, while offering a sense of freedom and independence that inpatient care often lacks.
Choosing outpatient addiction treatment offers several advantages that may appeal to individuals seeking flexible and accessible options for recovery. Here are some of the key advantages:
1. Flexibility
One of the primary advantages of outpatient treatment, like those of QuickSilver Counseling, is its flexibility. Participants can attend therapy sessions, counseling appointments, and support groups while living at home and maintaining their daily responsibilities, such as work, school, or caregiving. This flexibility allows individuals to integrate treatment into their existing schedules without needing an extended absence from their personal or professional lives.
2. Accessibility
Outpatient treatment programs are typically more accessible than residential or inpatient programs, which may require individuals to relocate or take time off from work or other obligations. With outpatient treatment, individuals can receive care from nearby facilities without significant travel or disruption to their daily routines. This accessibility ensures that treatment is more readily available to those facing logistical or financial barriers to entering residential programs.
3. Continued Community Connection
New Jersey outpatient rehab centers allow individuals to remain connected to their communities and support networks while undergoing treatment. Participants can draw upon the support of family, friends, peers, and community resources throughout their recovery journey. Maintaining these connections can provide valuable encouragement, accountability, and motivation, enhancing the individual’s well-being and belonging.
4. Cost-Effectiveness
Outpatient treatment is generally more cost-effective than residential or inpatient programs, making it a more affordable option for many individuals. Since outpatient programs do not require round-the-clock care or accommodation, they typically have lower associated costs. This cost-effectiveness can make treatment more accessible to individuals who may be concerned about the financial implications of seeking help for addiction.
5. Integration of Learning into Daily Life
Outpatient treatment allows individuals to practice the skills and strategies learned in therapy directly in their daily lives. By applying coping mechanisms, communication techniques, and relapse prevention strategies in real-world situations, participants reinforce their learning and build confidence in their ability to manage cravings and triggers outside of treatment sessions. This hands-on approach promotes skill-building and self-efficacy, empowering individuals to make sustainable changes.
6. Individualized Care
Prescription drug rehab New Jersey programs offer individualized care tailored to each participant’s unique needs and preferences. Treatment plans are developed based on comprehensive assessments and consider factors such as the individual’s substance use history, co-occurring mental health disorders, medical needs, social support system, and treatment goals. This personalized approach ensures that treatment aligns with the individual’s specific circumstances, challenges, and strengths, increasing the likelihood of successful outcomes.
7. Privacy and Confidentiality
Outpatient treatment allows individuals to receive care while maintaining privacy and confidentiality. Since participants do not reside in a treatment facility, they can attend therapy sessions and support groups without the concern of their absence being noticed by others. This can be particularly important for individuals who wish to keep their treatment discreet or have professional or personal responsibilities requiring privacy.
8. Less Disruption to Daily Life
Outpatient treatment minimizes disruption to individuals’ daily lives compared to residential or inpatient programs. Participants can continue to engage in their regular activities, such as work, school, or family responsibilities, while still receiving the support and treatment they need for their addiction. This can help individuals maintain a sense of normalcy and routine, benefiting their overall well-being and recovery process.
9. Greater Autonomy and Independence
Outpatient treatment empowers individuals to actively participate in their recovery journey and make decisions that align with their needs and preferences. Participants have greater autonomy and independence than residential programs, allowing them more control over their treatment experience. This level of self-determination can foster a sense of empowerment and ownership over one’s recovery process.
10. Gradual Reintegration into Society
Outpatient treatment supports individuals gradually reintegrating into their communities and transitioning back to their regular lives after completing treatment. By receiving care while living at home, participants can practice applying the skills and strategies learned in therapy to real-world situations. This gradual reintegration can help individuals build confidence, develop social connections, and navigate daily life challenges while maintaining sobriety.
Final Thoughts
Outpatient addiction treatment offers an exemplary approach for individuals struggling with substance abuse who also wish to maintain their everyday responsibilities. The flexibility, affordability, ability to practice skills in real-time, and the presence of a supportive network augment the ease of integration into a drug-free lifestyle. However, it is crucial to analyze personal needs, addiction severity levels, and available support systems before choosing this mode of treatment.